命令使用总结¶
命令相关¶
帮助¶
安装中文帮助
sudo aptitude install manpages-zh
Warning
中文帮助通常比较旧,内容过时。比如:某个选项其实已经无效了
使用英文帮助
alias eman='man -M /usr/share/man'
man 格式化并显示在线帮助手册页
>>> man file
另存man
>>> man file | col -b > file.txt
在gvim可以用
>>> :r! man file | col -b
查找¶
whatis - 在 whatis 数据库里查找完整的单词
>>> whatis file file (3tcl) - 操纵文件名和属性 file (1) - 确定文件类型
apropos - 在 whatis 数据库中查找字符串
>>> apropos file
状态¶
使用aptitude查看
>>> aptitude show file 软件包: file 状态: 已安装 自动安装: 否 版本号: 5.09-2 优先级: 重要 部分: utils 维护者: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com> 未压缩尺寸: 105 k 依赖于: libc6 (>= 2.4), libmagic1 (= 5.09-2) 描述: Determines file type using "magic" numbers File tests each argument in an attempt to classify it. There are three sets of tests, performed in this order: filesystem tests, magic number tests, and language tests. The first test that succeeds causes the file type to be printed. 主页: http://www.darwinsys.com/file/
使用dpkg查看
-s Report status of specified package.
>>> dpkg -s file Package: file Status: install ok installed Priority: standard Section: utils Installed-Size: 103 Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com> Architecture: i386 Version: 5.09-2 Depends: libc6 (>= 2.4), libmagic1 (= 5.09-2) Description: Determines file type using "magic" numbers File tests each argument in an attempt to classify it. There are three sets of tests, performed in this order: filesystem tests, magic number tests, and language tests. The first test that succeeds causes the file type to be printed. Original-Maintainer: Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-technologies.net> Homepage: http://www.darwinsys.com/file/
位置¶
type : 指示每个 name 将如何被解释
>>> type ls ls 是 'ls --color=auto' 的别名
>>> type type type 是 shell 内嵌
>>> type file file 已被哈希 (/usr/bin/file)
whereis : locate the binary, source, and manual page files for a command
>>> whereis file file: /usr/bin/file /usr/bin/X11/file /usr/share/file /usr/share/man/man1/file.1.gz
which : locate a command
>>> which file /usr/bin/file
dpkg : package manager for Debian
-L List files installed to your system from package-name.
>>> dpkg -L file /. /usr /usr/bin /usr/bin/file /usr/share /usr/share/bug /usr/share/bug/file /usr/share/bug/file/control /usr/share/bug/file/presubj /usr/share/doc /usr/share/doc/file /usr/share/doc/file/copyright /usr/share/doc/file/README.gz /usr/share/doc/file/README.Debian /usr/share/man /usr/share/man/man1 /usr/share/man/man1/file.1.gz /usr/share/doc/file/changelog.Debian.gz
压缩文件处理¶
解压bz2、gz、tgz。(bz2比gz 更小 )
tar xvzf file.tar.gz tar jvzf file.tar.bz2 tar xvzf file.tgz解压 rar
unrar x file.rar /tmp使用7z
7z x file.tar -o/tmp
标准输出、错误¶
通常我们看到的输出信息。其实是混杂着两种信息。输出(1)和错误(2)
>>> ls xxxxx / ls: 无法访问xxxxx: 没有那个文件或目录 /: bin dev initrd.img lost+found opt run srv usr vmlinuz.old boot etc initrd.img.old media proc sbin sys var cdrom home lib> 是 重定位符号。 默认是1,即标准输出。
下面的两条命令效果相同。
>>> ls > /tmp/rslt >>> ls 1> /tmp/rslt2> 表示将标准错误信息重定位。
2>&1 标准错误重定位到标准输出
2>1 会把错误信息写到一个叫 1 的文件. 囧oz
下面的命令是用wine启动FreeU21.exe. ignore the HUP (hangup) signal . 并把nohup命令的输出文件定位到 /dev/null
>>> nohup wine ~/.wine/drive_c/freegate/FreeU21.exe > /dev/null 2>&1 &
检索历史命令(显示行号)¶
cat
cat -b ~/.bash_history | grep ls !123history
history | grep lsalias
alias searchistory="history | grep "
按日期备份¶
tar cPizvf backup-`date +%Y%M%d-%S`.tar.gz /var/cache/apt/archives --exclude=/var/cache/apt/archivesapartial/* --exclude=/var/cache/apt/archives/lock
下载源码包¶
对某个软件的源码感兴趣,可以直接下载相关的源码。
apt-get source wmctrl如果不能自动解压,则需要安装dpkg-dev
sudo aptitude install dpkg-dev
Terminal下查看图片¶
就是用那个 图像查看器 。它对应的命令叫做 eog
eog 1.jpg
在终端下使用默认程序打开文件¶
大部分能搞定,但是pdf文件好像只能打开程序。
xdg-open unixs.gif
文件的三种时间¶
访问
更改
改动(权限)
查看
stat file
列出(ls)
改动(change)
ls -lc
访问(use)
ls -lu
更改
ls -l
查找(find)
按天数(三天之前)
find . -atime +3 find . -mtime +3 find . -ctime +3
按分钟(三分钟以内)
find . -amin -3 find . -mmin -3 find . -cmin -3
SSH隧道¶
| -N | 告诉SSH客户端,这个连接不需要执行任何命令。仅仅做端口转发 |
| -f | 告诉SSH客户端在后台运行 |
| -L XYZ | 将本地机(客户机)的某个端口转发到远端指定机器的指定端口 |
| -R XYZ | 将远程主机(服务器)的某个端口转发到本地端指定机器的指定端口 |
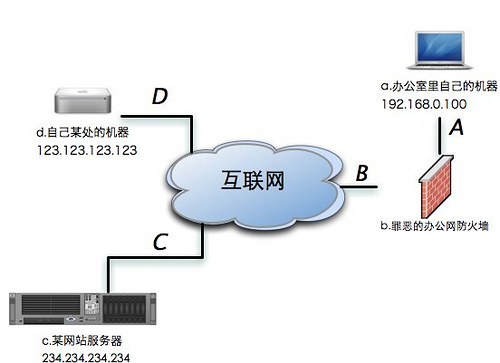
ssh本地隧道
将IP为Y的机器的Z端口通过中间服务器映射到本地机器的X端口。
ssh -N -f -L 2121:234.234.234.234:21 123.123.123.123
现在访问本地2121端口,就能连接234.234.234.234的21端口了
ftp localhost:2121
ssh远程隧道
把内部的Y机器的Z端口映射到远程机器的X端口上
ssh -N -f -R 2222:127.0.0.1:22 123.123.123.123
在IP是123.123.123.123的机器上我们用下面的命令就可以登陆公司的IP是192.168.0.100的机器了。
ssh -p 2222 localhost
SSH 翻墙¶
| -p | 指定远程主机的端口. 可以在配置文件中对每个主机单独设定这个参数. |
| -D | 指定一个本地机器 “动态的” 应用程序端口转发. 工作原理是这样的, 本地机器上分配了一个 socket 侦听 port 端口, 一旦这个端口上有了连接, 该连接就经过安全通道转发出去, 根据应用程序的协议可以判断出远程主机将和哪里连接. 目前支持 SOCKS4 协议, ssh 将充当 SOCKS4 服务器. 只有 root 才能转发特权端口. 可以在配置文件中指定动态端口的转发. |
| -T | 禁止分配伪终端 |
| -q | 安静模式, 消除所有的警告和诊断信息. |
常用翻墙命令
ssh -p 9999 -qTfnN -D 7070 onlybird@ssh.unssh.com